What Are Liabilities in Accounting? With Examples Bench Accounting
- admin
- January 18, 2021
- Bookkeeping
- 0 Comments

Sandra Habiger is a Chartered Professional Accountant with a Bachelor’s Degree in Business Administration from the University of Washington. Sandra’s areas of focus include advising real estate agents, brokers, and investors. She supports small businesses in growing to their first six figures and beyond. Alongside her accounting practice, Sandra is a Money and Life Coach for women in business.
Current portion of long-term debt
- Instead, these expenses are recorded as short-term liabilities on the company’s balance sheet until they are settled.
- Current or short-term assets are resources that can be converted into cash in a fiscal year or given operating cycle.
- It also includes accounts payable, dividends payable, notes payable, interest payments, and other short-term loans as well as taxes such as sales, payroll, income, and investment taxes.
- Some of the liabilities in accounting examples are accounts payable, Expenses payable, salaries payable, and interest payable.
- After earning income, taxes owed to the government are liabilities since paying taxes is an obligation.
Share capital is the sum realized from stock sale at its par value. Liabilities are categorized as current or non-current depending on their temporality. They can include a future service owed to others such as short- or long-term borrowing from banks, individuals, or other entities or a previous transaction that’s created an unsettled obligation. Self-invoicing is the process where the recipient of goods or services, rather than the supplier, generates the invoice.
Liabilities vs. Expenses

It is usually a simple, single sheet of paper summarizing your company’s assets, equity, and liabilities. In a small business, these usually are simple because they only pertain to basic things, like A/P, loans, salaries, and taxes. However, as your business grows and needs to comply with the US GAAP, there are other types that you must consider for accounting purposes. “Other” liabilities are any unusual debt obligations a company may have. These are typically minor, like sales taxes or intercompany borrowings. Accounting liabilities are recorded in the balance sheet under the liabilities section.
- The company must recognize a liability because it owes the customer for the goods or services the customer paid for.
- Liabilities are an integral part of the three basic financial statements used to report a company’s financial situation.
- Both the current and quick ratios help with the analysis of a company’s financial solvency and management of its current liabilities.
- In financial accounting this term refers to the amount of debt excluding interest.
- US GAAP requires some businesses to disclose or report contingent liabilities.
- But not all liabilities are expenses—liabilities like bank loans and mortgages can finance asset purchases, which are not business expenses.
Liabilities 101: Definition, Types, Examples and How to Calculate Them

The operating cycle refers to the period of time it takes for the business to turn its inventory into sales revenue and then back into cash, which helps cover these expenses. A well-managed operating cycle ensures that there is sufficient cash flow to meet these liabilities as they come due. Analysts and creditors often use the current ratio, which measures a company’s ability to pay its short-term financial debts or obligations. The ratio, which is calculated by dividing current assets by current liabilities, shows how well a company manages its balance sheet to pay off its accounting liabilities list short-term debts and payables. It shows investors and analysts whether a company has enough current assets on its balance sheet to satisfy or pay off its current debt and other payables. The current ratio measures a company’s ability to pay its short-term financial debts or obligations.

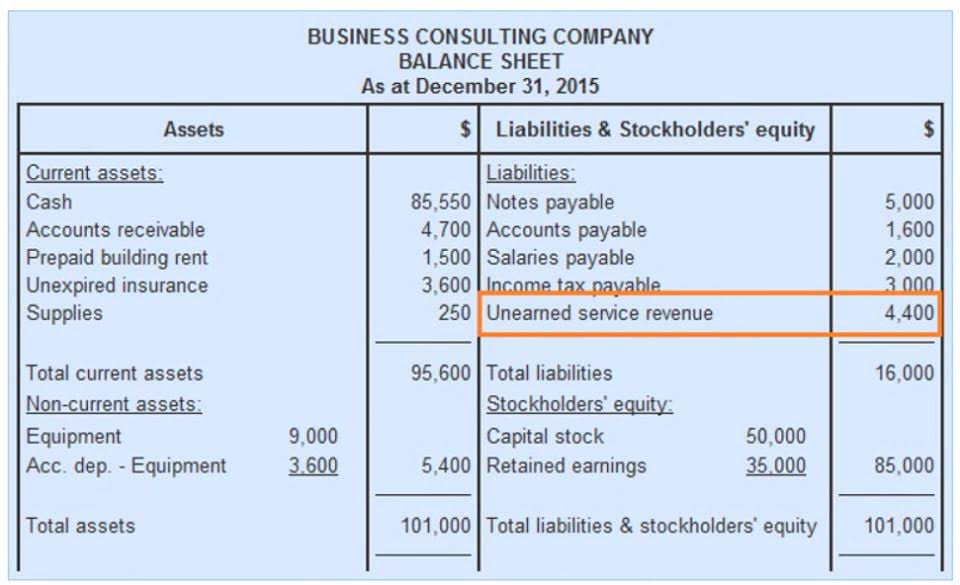
Accounts receivable is an asset account that comprises money owed to the company by its clients. Prepaid expenses are payments made in advance for products or services such as insurance, electricity, cable tv, and internet. Examples of liabilities are accounts payable, accrued liabilities, accrued wages, deferred revenue, interest payable, and sales taxes payable. An expense is the trial balance cost of operations that a company incurs to generate revenue.
- Furthermore, the ITC on RCM cannot be used to offset the initial tax payment—RCM liabilities must be settled in cash.
- Long-term liabilities include areas such as bonds payable, notes payable and capital leases.
- To calculate total liabilities, simply add up all of the liabilities the business has.
- When it comes to accounting processes for your small business, there can be a lot to know and understand.
- Current assets appear on a company’s balance sheet and include cash, cash equivalents, accounts receivable, stock inventory, marketable securities, prepaid liabilities, and other liquid assets.
Why Are Liabilities Important to Small Business?

Equity is the value of all the assets a company holds minus any money owed. These examples show how different transactions can result in both current and non-current accounting liabilities, depending on the type and timing of the liabilities. These obligations can offer insights into a company’s ability to manage its debts and its potential capacity to take on additional financing in the future. In conclusion, proper recognition and measurement of liabilities are essential for maintaining accurate and transparent financial statements. Understanding the criteria and measurement methods for liabilities helps organizations maintain a clear and confident financial position while facilitating informed decision-making. Here is a list of some of the most common examples of non-current liabilities.
What are 10 examples of assets?
Current liabilities are a company’s obligations that will come due within one year of the balance sheet’s date and will require the use of a current asset or create another current liability. Current Liabilities – Obligations which are payable within 12 months or within the operating cycle of a business are known as current liabilities. They are short-term liabilities usually arisen out of business activities. Examples of current liabilities are trade creditors, bills payable, outstanding expenses, bank overdraft etc.